(30358 products available)
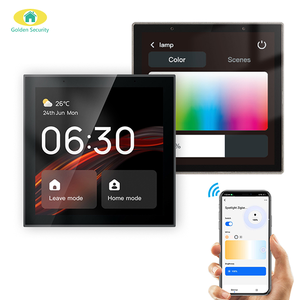
























































































































































































German industrial controls are factory automation parts used to start, stop, and control the operation of machines in a manufacturing setup. There are several kinds of German industrial machine controls designed for different applications.
Working Range
Usually, the working scope of a German wood lathe control can be described in controlling the length, diameter, as well as the workpiece variety. For example, control a workpiece length of up to 1000mm, a diameter of 300mm, and applicable to wood, bamboo, plastic, etc..
Precision
The precision German lathe control specifies the machining accuracy of the machining process. For example, achieve an accuracy of ±0.1mm, which can ensure the machining quality and the size requirement of the technician.
Power
The power German lathe control provides determines the maximum machining capacity and speed. For instance, a motor with a power of 1.5kW is sufficient to cope with normal machining needs and, at the same time, has stable control and high efficiency.
Speed range
The lathe can offer velocity variation is another significant characteristic. It can illustrate the lowest and highest applicable velocity of the machine, thus suitable for various materials and machining requirements. For example, the speed range goes from 50 to 2000RPM, enabling the machine to handle different workpiece kinds and machining techniques.
Machine Size
The dimension and weight of the lathe determine its establish and relocation range. For instance, a small-sized lathe weighs little and has dimensions that allow it to occupy a small area on the workshop floor, which permits one to store it easily, used, or relocated manual.
Proper maintenance is crucial to keep the machine working optimally, and the same goes for the German CNC control system. Here are some of the maintenance tips that can help.
Industrial automation:
German controls, like the Siemens S7, are widely used in industrial automation for process control, manufacturing, and factory automation. They can be applied to many automation systems, including assembly lines, food and beverage processing, packaging industries, and more.
Building automation:
German controls can be applied to building automation systems, realizing the control and management of this kind of building facilities such as HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning), lighting, security, and access control, etc. They enable functions like temperature regulation, energy management, alarm monitoring, and more, thus helping to enhance comfort, safety, and energy efficiency within buildings.
Transportation and vehicle control:
German control is widely used in the field of transportation and vehicle control. For example, automobile controllers are the "brains" of automotive systems. They are responsible for controlling the engine, transmission, braking system, etc., realizing vehicle performance, fuel efficiency, safety, and other functions. Additionally, German controls can also be applied to traffic management systems. Such systems may include traffic signal control, intelligent traffic management, and more. By German controls, traffic management authorities can regulate vehicle flow, alleviate traffic congestion, and enhance road safety.
Food and beverage industry:
German controls are commonly used in the food and beverage industry to control and manage food production and processing lines. For example, they can be applied to baking ovens. By German oven controls, bakers can program oven temperature, time, humidity, and other parameters to ensure the stability and quality of baked products. Besides, German controls can also be applied to beverage filling and packaging equipment, such as beverage bottling lines, to realize automatic control and management of the whole production process including filling, sealing, labeling, etc.
Plastic machinery:
German controls can be applied to plastic machinery, such as injection molding machines, extrusion machines, blow molding machines, etc. They are responsible for precise control of important processes, like material feeding, heating and plasticizing, injection and molding, cooling and demolding, etc. By utilizing German controls, plastic machinery can achieve accurate control of parameters like pressure, temperature, flow, and time, thereby ensuring stable operation and product quality.
Here are a few things to consider when choosing a German control:
Analysis the PLC Application:
Prioritize determining the distinct PLC application. This encompasses how well the PLC is capable of performing its programmed tasks. It also includes the specific industry or field in which its utilization is prevalent. Considering these factors can facilitate a more in-depth understanding of the effectiveness and importance of a PLC in various situations.
Choose the Right Model:
With the high performance, various types, and models of German PLC, it is critical to selecting a model that matches the project requirements, budget, and performance needs.
Networking Capabilities:
Pay attention to the communication and networking functions of the PLC, German PLC supports various industrial networks, such as Profibus, Ethernet, etc. Choose a PLC whose network function corresponds to the system requirement.
Determine the Environment:
Consider the working environment of the PLC, such as temperature, humidity, vibration, etc., and select a PLC with proper protective measures and environmental adaptability.
Find a Reliable Supplier:
Choose a reliable supplier to ensure it has a well-supported technical service and system upgrade capability.
Consider the Cost:
Finally, consider the cost of German PLC. Although its performance is strong, it is important to choose the model that matches the investment among many options.
Q1 What is German control PLC?
A1. A programmable logic controller (PLC) is a digital control system used to automate industrial processes. The PLC is designed to be used in a wide range of applications and can be easily programmed to meet specific needs. German PLCs are typically used in manufacturing and assembly lines, but they can also be found in other industries such as oil and gas, water and wastewater treatment, power generation, and transportation.
Q2 How Does German Control Work?
A2. A PLC works by receiving input from sensors or other devices connected to it. These inputs are then processed according to the programmed logic within the PLC. The result of this processing is output signals that are sent to actuators or other devices to carry out specific actions. For example, a temperature sensor might be connected to a PLC as an input device. The PLC may be programmed to turn on a heater if the temperature drops below a certain level. The heater would then be an output device connected to the PLC.
Q3 What Are The Advantages of German Control?
A3. There are many advantages to using PLCs in industrial automation. One advantage is that they are very flexible and can be easily reprogrammed to accommodate changes in production processes or equipment. Additionally, PLCs can be networked together so that multiple controllers can be managed from a single central location. This networking capability allows for easy data sharing and collection, as well as remote access to the system for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes. Other benefits of a PLC include high reliability, ease of installation, low maintenance requirements, and cost-effectiveness.
Q4 What Are The Disadvantages of German Control?
A4. While there are many advantages to using PLCs, some drawbacks exist. One disadvantage is that the initial cost of purchasing and installing a PLC system can be high compared to other types of control systems. In some cases, the complexity of a PLC system may also make it more difficult to troubleshoot and repair if problems should occur. Proper planning, design, and implementation are essential to minimizing these risks.
Q5 What Are The Major Components Of A PLC?
A5. The main components of a PLC include the following: