(118302 products available)








































































































































































































A chiller machine controls the temperature of liquids through the process of heat exchange and absorbs heat from liquids through evaporation. According to how energy is supplied, how heat is exchanged, and how refrigeration is produced, chiller machines can be classified into different types.
The chiller machine has many specifications to consider when buying it. Here are some key aspects that may affect the performance of the chiller.
Capacity
It refers to the amount of heat each machine can remove from a space in one hour and is usually measured in tons or kilowatts. One ton of cooling equals a removal of 3.517 kilowatts of heat. A one-ton chiller can remove heat produced by about 1,000 BTUs (British thermal units) per hour.
Compressor Type
There are different types of compressors for chillers: reciprocating, screw, centrifugal, and scroll. The specific type will impact the chiller's energy efficiency, noise level, and operating range.
Condenser Type
A chiller can be of an air-cooled or water-cooled type. This option will affect how the machine dissipates heat into the surrounding environment.
Energy Efficiency
A cooling machine's energy efficiency is the ratio of cooling output to the electrical energy input. It is otherwise known as EER (energy efficiency ratio) or COP (coefficient of performance). Choosing a chiller with a high EER or COP will help to reduce energy costs significantly.
Operating Temperature Range
Each chiller machine has a specific temperature range within which it operates efficiently. This range can differ depending on the type and design of the chiller. For optimal cooling performance, it is necessary to operate within the specified temperature range and not exceed the limits defined by the manufacturer.
Regular maintenance will help to ensure the chiller machine works great and continues to deliver efficient cooling. Here are some tips on maintenance to keep the machine in good shape.
Regular Inspections
Users should carry out routine inspections. This process helps to discover potential troubles early and quickly fix them before they become major issues. The inspections should include examining critical parts like the condenser, evaporator, compressor, and expansion valve for signs of wear, damage, or leaks. Also, check that there are no refrigerant leaks around the chiller area.
Clean the Chiller
Taking care of the dirt and debris that gathers on the chiller unit's surface will improve heat exchange efficiency. Air-cooled condensers, in particular, are prone to fouling. Cleaning them improves airflow and cooling performance, too.
Lubrication of Moving Parts
Constantly moving parts like the compressor bearings require regular lubrication. Lubrication reduces friction and avoids premature wear, extending the lifespan of the chiller.
Calibration
With time, the sensors and controls of the chiller may drift from their original settings. This drifting can affect the machine's efficiency and cooling capacity. So, there is a need to routinely calibrate the sensors and controls. Doing this helps to optimize performance and maintain the cooling capacity.
As an important part of industrial cooling, the chiller is suitable for various industries and fields. According to different industry needs, each type of chiller plays its irreplaceable role.
Machinery industry:
Chillers are essential cooling equipment for the mechanical industry. They are mainly used to cool and solidify the molds during mold manufacturing and injection molding. By controlling the cooling rate and temperature of the molds, chillers help improve molding efficiency, product quality, and manufacturing precision. They also prevent overheating and prolong the service life of the equipment.
Food processing:
In the food and beverage processing industry, water chillers ensure the stable production and quality of products by maintaining refrigeration systems' cooling, fermentation, and freezing processes. They also rapidly cool food and beverages to extend shelf life and comply with food safety standards.
Plastic industry:
Chillers play an indispensable role in plastics production: temperature control. Whether it is blow molding, injection molding, or extrusion molding, maintaining the optimal temperature is crucial for product quality and production efficiency. Chillers also permit to cool molds rapidly and control water temperature used in plastics processing.
Electronics industry:
Chillers are used to cool down various equipment and production lines in electronics manufacturing, such as computer servers, data storage, and telecommunications equipment. They help maintain equipment operation and prevent overheating, ensuring the stable operation of electronic products.
Chemical industry:
Chillers are frequently used in chemical production and processing, such as reaction cooling, distillation, extraction, and crystallization. They can control reaction temperatures during chemical production to ensure reaction stability and yield. Moreover, they can cool down equipment and reactors to prevent overheating and ensure safety.
Choosing the right chiller machine can be an uphill task for businesses. With numerous options available, it can be tough to determine what type and size of chiller is suitable for a particular application.
The first step in selecting a chiller is to analyze the facility's cooling demand. This can be done by conducting a cooling load analysis. Businesses may choose to hire an HVAC engineer to help them better understand the facility's cooling demand. An cooling load analysis takes into consideration a number of factors including temperature, humidity, equipment, and square footage of the facility. A cooling load analysis will help determine the chiller's capacity needed to adequately cool the space or process.
Once the cooling load has been established, the next step is to choose the right type of chiller. Consider factors such as location, application, efficiency goals, and budget. If the facility is in a warm, dry climate, an air-cooled chiller may be more suitable. However, for high cooling demands or industrial processes, a water-cooled chiller may be ideal.
After choosing the type of chiller, the size must be determined. It is important to note that undersized or oversized chillers can negatively impact performance, efficiency, and control. Consult with an HVAC professional to help determine the best size chiller for the facility. If the facility may undergo expansion in the future, it is best to consider that when determining the cooling load.
When it comes to selecting a chiller, consider the efficiency of the machine. While more efficient machines may have a higher upfront cost, they can save the business a lot of money over time. Businesses can calculate operational costs over the lifespan of the chiller to get a better understanding of how much it will cost.
Finally, the brand and model of the chiller must be selected. Research different manufacturers and read reviews to find a reliable, high-performing chiller. It may also be helpful to get recommendations from HVAC experts. Consider the required features and controls for the application and review warranty details to ensure the chiller is protected from damages.
Q1: What is the difference between a chiller and a refrigerator?
A1: While both are cooling machines, the working temperature is the main difference between a chiller machine and a refrigerator. Chillerschillers generally use refrigerants, such as ammonia, that can provide colder temperatures. Therefore, refrigerators are generally suitable for food products; chillers can be used to process and preserve food and drink products.
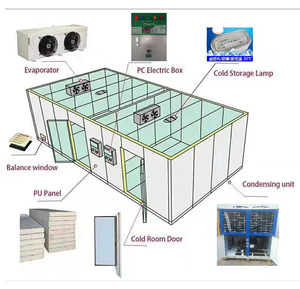
Q2: What are the main components of a chiller machine?
A2: A chiller machine has the following key components:
Q3: How long can a chiller machine operate continuously?
A3: Generally, if the machine is well maintained, there is no specific limit to how long a chiller can run continuously. Many chillers across the world run continuously for about five to ten years.