(1405 products available)
















































































































































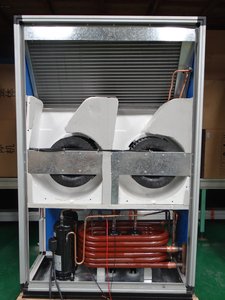





































































A big water chiller is a machine designed to reduce the temperature of water through the removal of heat, resulting in cold or chilled water. This chilly water is then used for cooling purposes, such as industrial machinery, processing equipment, large-scale air conditioning systems, and the injection molding industry, to name just a few. Water chillers can be based on three different technologies – absorption, screw, and centrifugal:
Industrial chillers provide specifications for different components and parts to help users understand what they can expect when buying one. A big water chiller's specification will likely include the following details:
Cooling Capacity
A big water chillers' cooling capacity indicates the maximum amount of heat it can absorb from the circulating water per unit of time. Manufacturers represent the cooling capacity of chillers using tons (1 ton = 12,000 BTU per hour).
Evaporator and Condenser
The type of evaporator and condenser can influence how a water chiller works. For example, some condensers might be more suited to outdoor use because they require air from the surroundings to work effectively.
Compressor
Chillers can have different types of compressors that can produce varying levels of cooling capacity, pressures, and efficiencies. The specification can also include the refrigerant the compressor uses.
Power Consumption
A big water chillers' power consumption is crucial for understanding operating costs. It is influenced by many factors, including the cooling capacity, the type of compressor, and the efficiency rating.
Operating Temperature
Big water chillers normally have an evaporator temperature range of -50°C to 15°C and a condenser temperature range of 0°C to 55°C. The precise figures may differ by manufacturer and model.
Like any other machine, chillers need maintenance so they can continue to deliver efficient cooling. Regular maintenance helps prevent small issues from becoming costly repairs. Here's a brief look at some of the more common maintenance tasks required for big water chillers:
Inspecting Components
A technician will look at a chiller’s system components to see if there are any signs of wear, rapture, leaks, corrosion, or other issues that could affect performance.
Cleansing Components
Some parts of a chiller may need to be cleaned from time to time to remove dirt and debris that could affect efficiency and performance. Condenser coils, in particular, are more effective when clean.
Lubricating Moving Parts
Lubrication helps prevent unnecessary wear and tear. Ideally, the grease should be suitable for operating in low temperatures.
A big water chiller has many applications in diverse industries. The majority of process industries use water chillers to cool hot products, equipment, and machines. In the food and beverage industry, water chillers cooling beverages such as beer, juices, and sodas. They also cool dairy products such as milk and ice cream. Boxed or bottled drinks cool down to a specific temperature and must be the controlled exactly to ensure product quality and avoid spoilage.
The chemical processing industry and pharmaceutical use water chillers to maintain precise temperatures during chemical reactions and equipment operation. In oil refineries, water chillers control the temperature of oil while it is being processed, helping improve the viscosity and quality.
Water chillers are used in commercial and industrial facilities. They are integrated into HVAC systems to provide cool air when necessary. In large commercial buildings and hotels, air conditioning must be optimal and efficient. Furthermore, water chillers look after machines without any moving parts that may overheat, especially when they are working continuously. Some water chillers can adjust humidity and dehumidify areas bordering about 50-60% relative humidity to prevent mold growth.
Big water chillers also support critical systems like data centers, hospitals, universities, and laboratories, where precise control of equipment and the room must be maintained. They also enable the safe storage of sensitive products like medical supplies, chemicals, and perishable goods.
Big water chillers are essential components of many manufacturing plants and the machining industry. They are used primarily in machine tools to maintain engraving, cutting, and milling machines at a constant temperature during the machine's operation to ensure product quality and avoid the risk of tools and machines becoming worn out quickly.
Another application of big water chillers is plastic molding and extrusion. They cool down molds in which liquid plastic is solidified into specific shapes and used to make plastic pieces, parts, and products that are used in almost everything around the home and office.
Water chillers are also found in laser cutting and welding machines that require precise temperature controls to achieve ideal results when cutting and joining metal parts and substrates. Moreover, they are used in refrigeration production lines to cool down the refrigerant while it is being processed before use in refrigerators and air conditioners.
The following tips may help business buyers in selecting the most suitable industrial water chillers for their needs:
Understand Processes and Load
The first step in choosing a chiller is to verify cooling requirements. Analyze the heat loads, temperature ranges, and volume of processed water. Most industrial processes generate heat that needs to be removed to continue operating efficiently. Knowing how much heat (BTUs/hr) needs to be removed will help narrow the search to chillers with suitable cooling capacities. Take into account fluctuations in heat loads and consider selecting a chiller that has a capacity higher than average for future expansion.
Consider Reliability
Chillers are critical components of many industrial processes. Select these with a focus on reliability and minimal downtime. Opt for proven equipment from reputable manufacturers. Look for features that enhance reliability, such as quality construction, robust compressors, and premium refrigerant options. Also, consider chillers with built-in redundancy, like dual compressors or backup cooling loops, to maintain operation during equipment maintenance or unexpected failures.
Pay Attention to Efficiency
A chiller will consume energy continuously during operation, so its energy efficiency will impact operating costs. Choose these with efficient cooling systems, like variable-speed drives for compressors and high-performance heat exchangers. Consider the EER and IPLV rating of the chiller, which evaluates its efficiency at different loads and gives a better indication of real-world performance than the EER alone. Also, Optimize chiller placement to reduce energy used for cooling. Locate these close to heat sources that need cooling to minimize the length of piping required. Shorter piping minimizes resistance to water flow and reduces the energy needed to pump water.
Investigate Co-Generation and Waste Heat Recovery Options
Co-generation is generating electricity by using the thermal energy from a chiller's condenser. This process makes a chiller more efficient since it utilizes a byproduct (waste heat) of cooling to generate power. Some industrial chillers come with thermal energy that can be used to drive turbogenerators to generate electricity that can be used to offset a facility's power needs or sold to the grid. Doing this would create a decentralized electric generation system that is more efficient and cost-effective than traditional methods.
Assess Equipment Size and Footprint
To make sure it can house a chiller, consider its basement, plant, or roof spaces. Select a chiller with a compact design that can easily fit into the limited space available. Also, Check accessibility for maintenance and ensure service technicians have sufficient space to work on the chiller components. In addition, Examine the weight and hoisting capabilities of the equipment to be sure the lifting gear used can safely lower or raise the chiller into position.
Q: How does a big water chiller cool water?
A: A big water chiller uses a refrigeration cycle to cool water. It evaporates refrigerant to absorb heat from the water in the evaporator. The water absorbs heat and gets cooled down. The refrigerant, after absorbing heat, becomes gas and is compressed by the compressor. The gas is then condensed into liquid by rejecting heat to the surroundings using air or water in the condenser. The liquid refrigerant then goes back to the evaporator, and the cycle repeats.
Q: Is a big water chiller the same as a cooling tower?
A: No. A big water chiller and a cooling tower are not the same. A cooling tower is actually another device that removes excess heat from water by vaporizing a small amount of water. While both a water chiller and a cooling tower cool water, their cooling processes and mechanisms are different.
Q: Is a big water chiller the same as an氟 chiller?
A: No. A big water chiller and a氟 chiller are not the same. A氟 chiller, also known as a direct air cooling chiller, cools air directly by circulating refrigerant through evaporating coils. A big water chiller cools water, and the chilled water are then circulated through coils to cool air.
Q: How big are commercial water chillers?
A: Commercial water chillers are usually large. Many big water chillers are the size of a container or bigger. They can be easily around 2.4m to 3m in height. Some can even reach 4m in height. They are huge industrial-grade equipment.